
- #WHAT IS INTEL MANAGEMENT ENGINE CHIPSET DRIVER#
- #WHAT IS INTEL MANAGEMENT ENGINE CHIPSET FULL#
- #WHAT IS INTEL MANAGEMENT ENGINE CHIPSET CODE#
#WHAT IS INTEL MANAGEMENT ENGINE CHIPSET CODE#
That failure creates a window of opportunity for other chip components, such as the Integrated Sensor Hub, to execute malicious code that runs very early in the boot process with the highest of system privileges. The bug stems from the failure of the input-output memory management unit-which provides protection preventing the malicious modification of static random-access memory-to implement early enough in the firmware boot process. Often abbreviated as CSME, this feature implements the firmware-based Trusted Platform Module used for silicon-based encryption, authentication of UEFI BIOS firmware, Microsoft System Guard and BitLocker, and other security features. The flaw resides in the Converged Security and Management Engine, a subsystem inside Intel CPUs and chipsets that’s roughly analogous to AMD’s Platform Security Processor. While Intel has issued patches to lessen the damage of exploits and make them harder, security firm Positive Technologies said the mitigations may not be enough to fully protect systems. For IPv6, the Intel ME actually has its own address that is not shared with the host.Virtually all Intel chips released in the past five years contain an unfixable flaw that may allow sophisticated attackers to defeat a host of security measures built into the silicon. Note that for the networking services, for IPv4, the host OS shares the same network address with the Intel ME. In one touch, organization must configure their own certificates, symmetric keys, and trusted hosts that can then be used to complete deployment remotely. This is done through firmware-embedded certificate anchor keys for well-known certificate authority.
In zero touch, well-known certificate authority keys can be used to validate IT credentials automagically and take ownership.
#WHAT IS INTEL MANAGEMENT ENGINE CHIPSET FULL#
#WHAT IS INTEL MANAGEMENT ENGINE CHIPSET DRIVER#
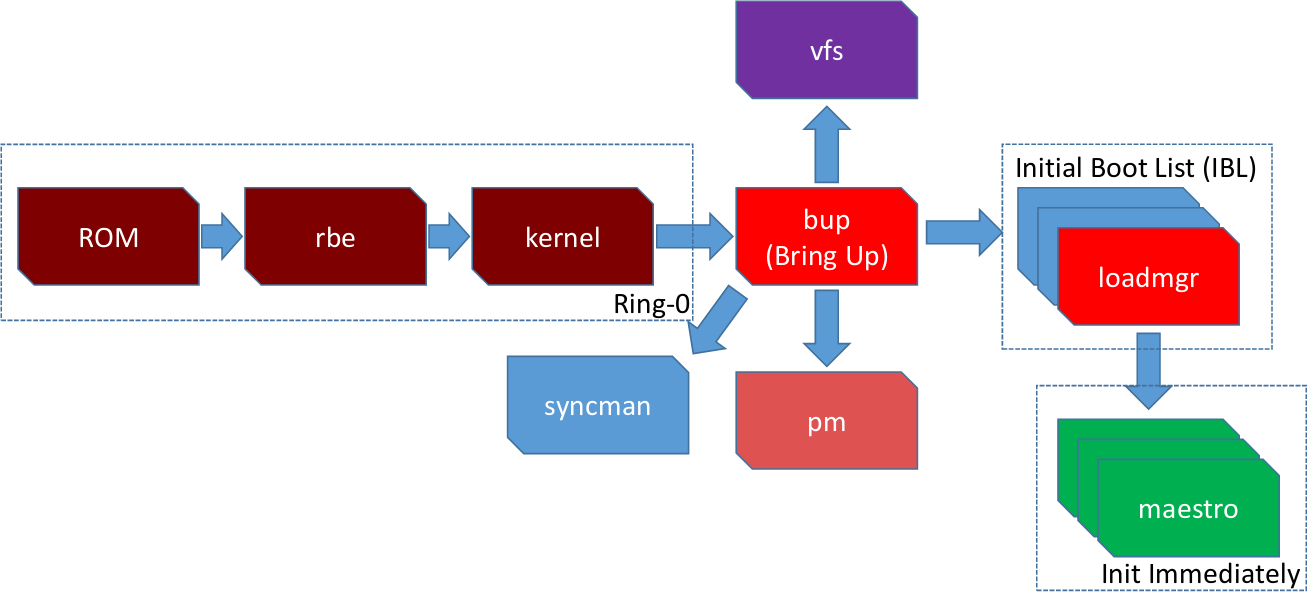
ME was connected to both the host driver through an internal bus called the Host Embedded Controller Interface ( HECI). Data is encrypted in AES-CTR mode using the platform container key (PCK). Persistent data was stored in flash memory which was accessible by the SPI bus which stored things such as Intel's AT-d metadata. The MCU supported SRAM and DRAM that is isolated from the host processor. The firmware that was running was developed internally by Intel and provided key management support, access control, and other administrative services. Originally, ME was a 32-bit ARCompact microcontroller running ThreadX, a real-time OS. ME has a dedicated connection to the network interface, in theory allowing it to intercept, send, and receive data without the processor's knowledge (or any software/OS knowledge).įor modern systems, Intel has switched to using their own x86 Quark microcontroller.
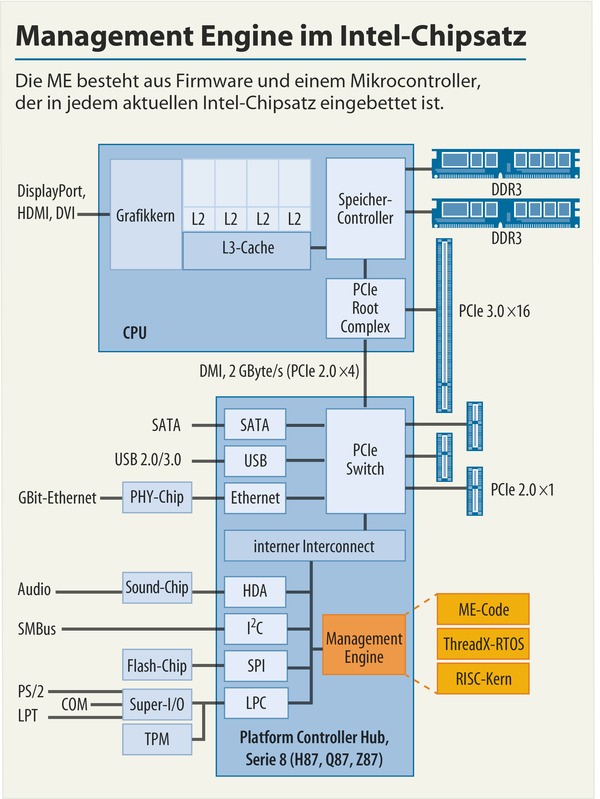
ME can remain active during power off, idle states, and reboots of the main processor. ME shares the flash with the BIOS, but is otherwise independent. ME is an independent coprocessor, relying on just itself. Since the 2009, with the introduction of the Core family, ME can be found in all PCHs, meaning it is present on all Intel embedded, mobile, and desktop parts. ME was originally integrated into the MCH as bar of Intel's 965 Express chipset which were introduced back in June 2006. ME provides all the necessary functionality needed to provide many of Intel's advanced security and many of the root of trust services. Intel's Management Engine (ME or IME) is a coprocessor implemented as a dedicated microcontroller embedded into the same die as the chipset.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
